Determining what constitutes a “good” homeowners insurance rate in the US isn’t as straightforward as finding the lowest number. Numerous factors influence the premium, meaning what’s considered a good rate for one homeowner might be exorbitant for another. Understanding these factors and how they affect your premium is key to securing adequate coverage at a reasonable price. This article will explore the elements that impact homeowners insurance rates and provide guidance on how to assess whether you’re getting a good deal.
Factors Influencing Homeowners Insurance Rates
Several elements contribute to the cost of homeowners insurance. Insurers assess risk based on these factors to determine the likelihood of a claim and the potential cost of that claim.
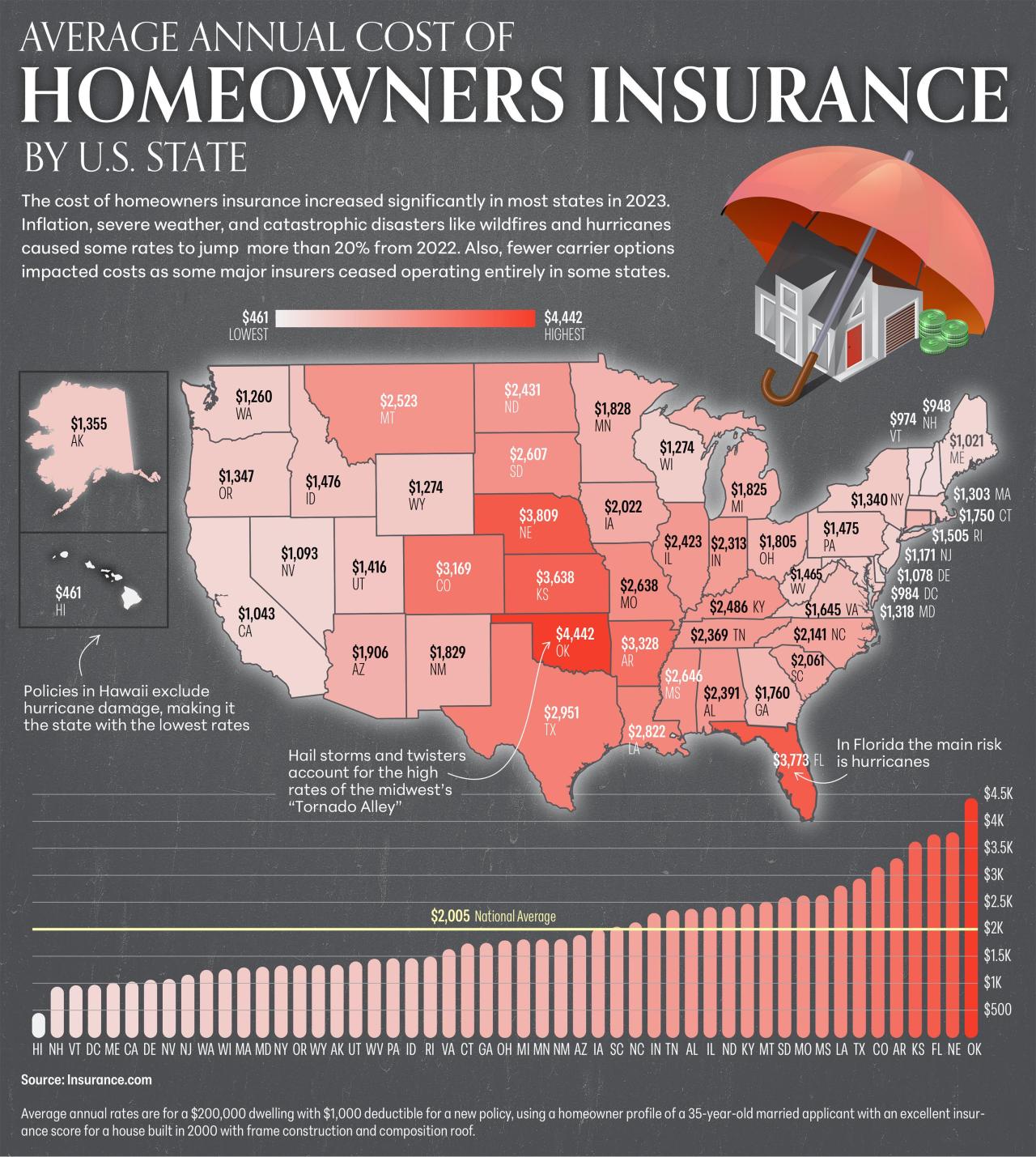
Location and Risk Factors: Your geographic location is a major determinant of your insurance rate.
- Insurers analyze crime rates in your area; high crime areas typically lead to higher premiums due to the increased risk of theft and vandalism.
- Areas prone to natural disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, earthquakes, or wildfires will also see higher rates to compensate for the increased risk of property damage.
- Flood zones are another critical consideration. If your property is in a designated flood zone, you may require separate flood insurance, which can significantly increase your overall insurance expenses.
Home Characteristics: The specifics of your home itself play a significant role.
- The age of your home matters. Older homes often have outdated systems (electrical, plumbing) that are more prone to failure, leading to higher insurance costs.
- The materials used in your home’s construction affect the premium. Homes built with fire-resistant materials like brick or concrete are generally cheaper to insure than those constructed primarily of wood.
- The size of your home and the number of rooms, particularly bedrooms and bathrooms, influence the coverage amount needed and therefore the premium.
- Features like a flat roof (or a roof with a significant flat portion) can increase premiums due to the potential for water pooling and subsequent damage.
Coverage Amount and Policy Options: The level of coverage you choose directly impacts your rate.
- Dwelling coverage should reflect the cost to rebuild your home if it were completely destroyed. It’s crucial to calculate this accurately, as underinsuring can leave you with significant out-of-pocket expenses in the event of a major loss.
- Personal property coverage protects your belongings. Accurately estimating the value of your possessions is important.
- The deductible (the amount you pay out of pocket before the insurance company covers the rest) also influences the premium. A higher deductible generally results in a lower premium, but you need to be comfortable paying that amount if you file a claim.
Personal Factors: Your individual circumstances can also affect your insurance rate.
- Your claims history is a key factor. If you’ve filed multiple claims in the past, insurers view you as a higher risk and will likely charge higher premiums.
- Your credit score is used by some insurers to assess risk. A lower credit score may result in a higher premium.
- Occupancy matters. If your home is frequently unoccupied (e.g., a vacation home or rental property), it’s considered a higher risk due to the increased potential for undetected damage or theft.

What is Considered a “Good” Rate?

Given the numerous variables, defining a “good” rate requires benchmarking and comparison. Here’s how to approach it:
Obtain Multiple Quotes: The most effective way to gauge whether you’re getting a good deal is to obtain quotes from multiple insurance companies. Compare the coverage levels, deductibles, and premiums offered by each insurer.
Compare with Averages: Research the average homeowners insurance rates in your state and zip code. Numerous online resources provide this information. Keep in mind that these are just averages and your specific circumstances may result in a higher or lower rate.
Assess Coverage Adequacy: Don’t focus solely on the premium. Ensure the policy provides adequate coverage for your home and possessions. Underinsuring to save money can be a costly mistake in the long run. Consider the following:
- Will the policy cover the full cost to rebuild your home?
- Does the personal property coverage adequately protect your belongings?
- Does the policy include liability coverage to protect you if someone is injured on your property?
Evaluate Discounts: Ask about potential discounts. Many insurers offer discounts for things like:
- Installing security systems, smoke detectors, and other safety features
- Bundling your homeowners insurance with auto insurance
- Being a long-term customer
- Paying your premium annually
Consider the Insurer’s Reputation: Price isn’t everything. Choose an insurer with a good reputation for customer service and claims handling. Check online reviews and ratings to get a sense of the insurer’s performance.
Strategies to Lower Your Homeowners Insurance Rate
Even if your initial quotes seem high, there are steps you can take to potentially lower your homeowners insurance rate:
Improve Home Security: Installing a security system, burglar alarm, and high-quality locks can deter theft and reduce your risk, leading to lower premiums.
Increase Your Deductible: Opting for a higher deductible can significantly lower your premium. Just ensure you can comfortably afford to pay the deductible if you need to file a claim.
Maintain Your Home: Regular maintenance can prevent costly repairs and reduce the risk of claims. Keep your roof in good condition, address plumbing leaks promptly, and ensure your electrical system is up to code.
Review Your Coverage Annually: As your circumstances change, your insurance needs may also change. Review your coverage annually to ensure it still meets your needs and that you’re not paying for unnecessary coverage.
Shop Around Regularly: Don’t simply renew your policy each year without shopping around. Insurance rates can change, so it’s wise to compare quotes from multiple insurers at least once a year to ensure you’re still getting the best deal.
Ultimately, a “good” homeowners insurance rate is one that provides adequate coverage at a competitive price, from a reputable insurer. By understanding the factors that influence your premium and taking steps to mitigate your risk, you can increase your chances of securing a policy that meets your needs without breaking the bank.





Leave a Reply